
FIBROSCAN
FIBROSCAN
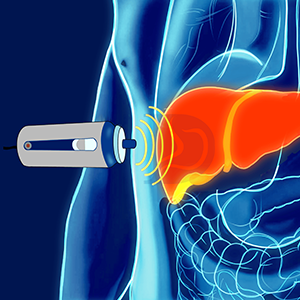
FibroScan, also known as transient elastography, is a non-invasive medical device that measures liver stiffness to assess liver health. Here's an overview:
Types of FibroScan
1. Liver FibroScan : Measures liver stiffness to assess liver fibrosis.
2. Liver Steatosis Assessment : Measures liver fat content to assess liver steatosis.
Procedure
1. Preparation : Patient fasts for 2-3 hours before the procedure.
2. Probe Placement : A probe is placed on the patient's abdomen.
3. Measurement : The device sends vibrations through the liver and measures the stiffness.
4. Results : Liver stiffness is measured in kilopascals (kPa).
Indications
1. Liver Fibrosis : Diagnose and monitor liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease.
2. Liver Steatosis : Diagnose and monitor liver steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
3. Liver Cancer Screening : Identify patients at risk of liver cancer.
Benefits
1. Non-Invasive : No needles or incisions required.
2. Quick and Painless : Procedure takes around 10 minutes.
3. Accurate : Correlates well with liver biopsy results.
4. Repeatable : Can be repeated multiple times to monitor liver health.
Limitations
1. Obesity : May affect accuracy in obese patients.
2. Ascites : May affect accuracy in patients with ascites.
3. Liver Iron Overload : May affect accuracy in patients with liver iron overload.
Interpretation of Results
1. Liver Stiffness : Measures liver fibrosis, with higher values indicating more severe fibrosis.
2. Liver Fat Content : Measures liver steatosis, with higher values indicating more severe steatosis.
Clinical Significance
1. Liver Fibrosis Staging : FibroScan results can be used to stage liver fibrosis.
2. Treatment Monitoring : FibroScan results can be used to monitor treatment response.
3. Liver Cancer Risk Assessment : FibroScan results can be used to assess liver cancer risk.
