
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
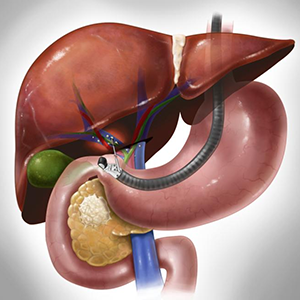
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) is a minimally invasive procedure that combines endoscopy and ultrasound to examine the gastrointestinal tract and nearby organs. Dr. Yogesh Bade, a trusted gastroenterologist in Hinjewadi, Wakad & Ravet, Pune, performs EUS for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Diagnostic Applications
1. Gastrointestinal cancer staging : Evaluate tumor size, depth, and spread.
2. Pancreatic disorders : Diagnose pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, and cysts.
3. Gastrointestinal wall abnormalities : Evaluate thickening, inflammation, or tumors.
4. Submucosal lesions : Diagnose lesions, such as gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs).
Therapeutic Applications
1. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) : Collect tissue samples for cytology or histology.
2. Fine-needle injection (FNI) : Inject therapeutic agents, such as chemotherapy or antibiotics.
3. Celiac plexus block : Relieve abdominal pain by injecting a neurolytic agent.
4. Pancreatic pseudocyst drainage : Drain fluid collections in the pancreas.
Procedure
1. Preparation : Patient fasts for 6-8 hours before the procedure.
2. Sedation : Patient receives sedation to relax during the procedure.
3. Endoscope insertion : The endoscope is inserted through the mouth and guided to the target area.
4. Ultrasound imaging : High-frequency sound waves produce detailed images of the digestive tract and surrounding tissues.
5. Biopsy or intervention : The endoscopist performs a biopsy, FNA, FNI, or other therapeutic interventions as needed.
Benefits
1. Minimally invasive : Reduces risk of complications and recovery time.
2. High-resolution imaging : Provides detailed images of the digestive tract and surrounding tissues.
3. Accurate diagnosis : Enables accurate diagnosis and staging of gastrointestinal disorders.
4. Therapeutic interventions : Offers minimally invasive treatment options for various conditions.
Risks and Complications
1. Bleeding : Risk of bleeding from biopsy or intervention.
2. Infection : Risk of infection from biopsy or intervention.
3. Pancreatitis : Risk of pancreatitis from EUS-guided interventions.
4. Adverse reactions : Risk of adverse reactions to sedation or other medications.
